Some rules to avoid scams.
1. Read emails carefully.
If you receive an email from a company or other, read it to analyze if it is not a scam because you can easily recognize certain types of scams thanks to the presence of:
– email address of the company that seems crazy (exemple: ups@raccara.com) Exemple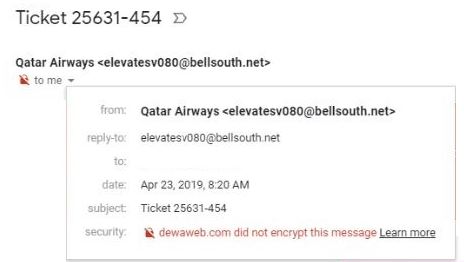
– spelling errors in the company name;
– gross spelling mistakes Exemple
– obvious grammatical errors Exemple
– strange writing fonts Exemple;
– request to share personal information Exemple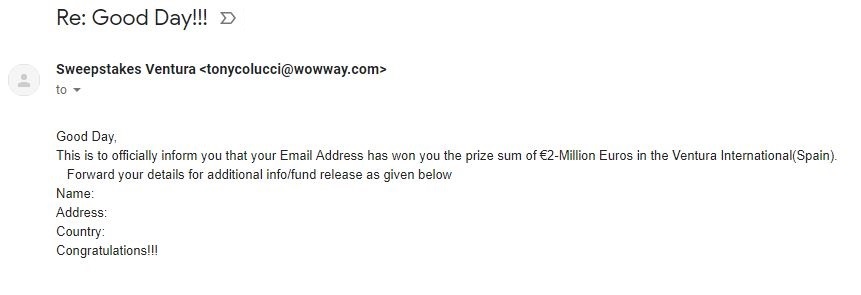
– request for payment information (bank account etc…);
– presence of a response RE in the title of the email when you have never contacted this person Exemple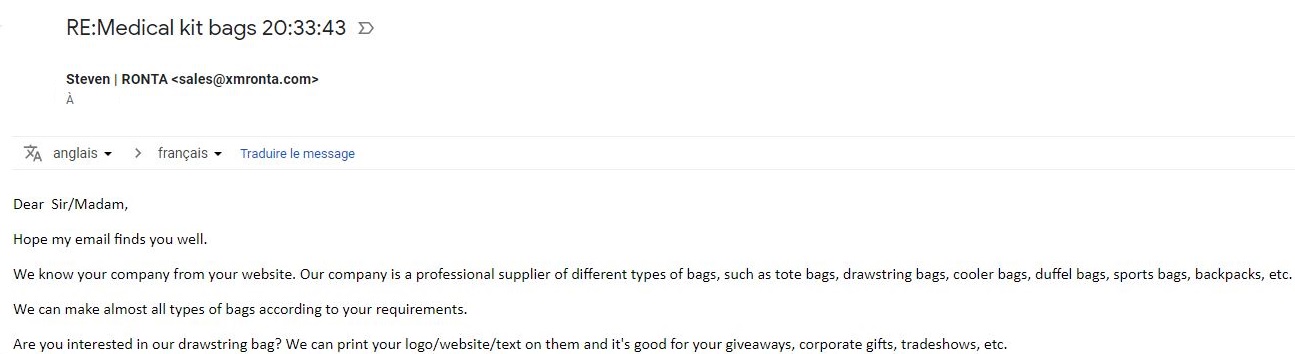
– proposals to purchase goods that do not interest you (cryptocoins, email list, etc….) Exemple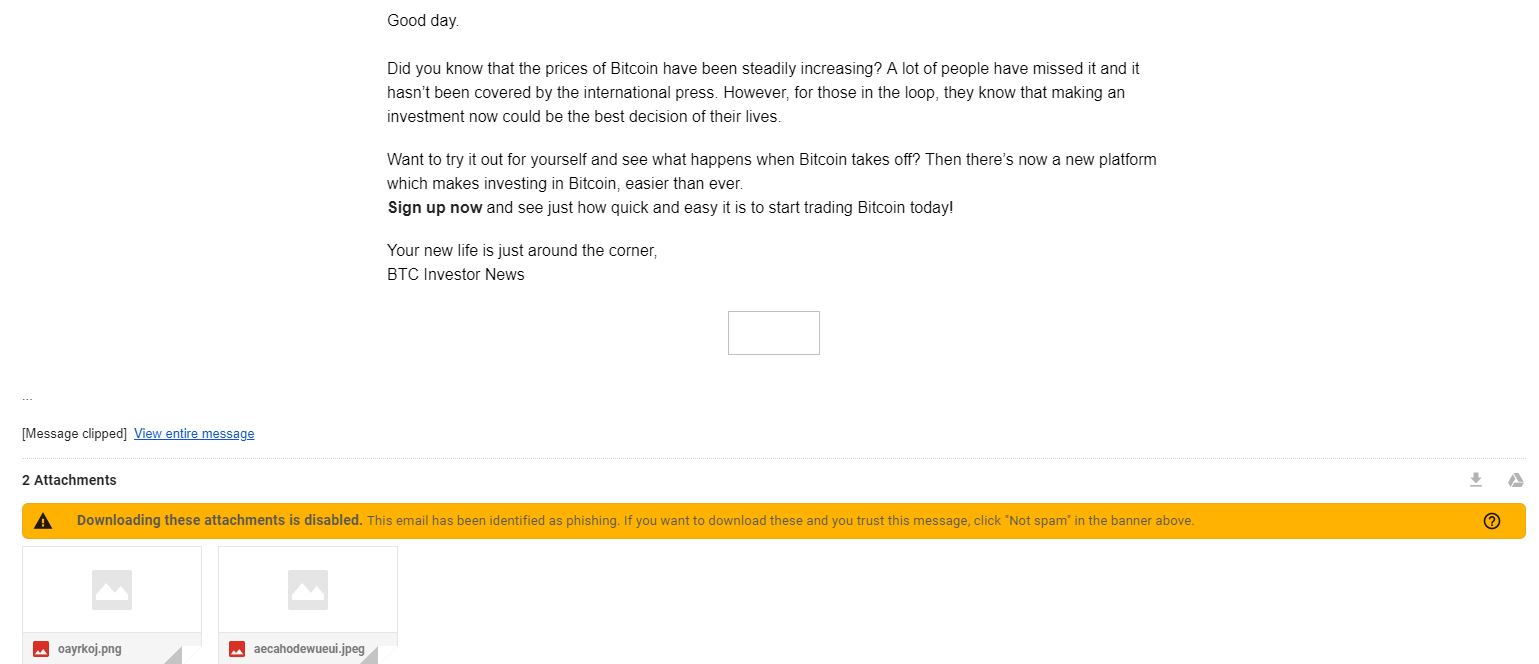
– money request from a person posing as a friend (mainly via Western Union or by card) Exemple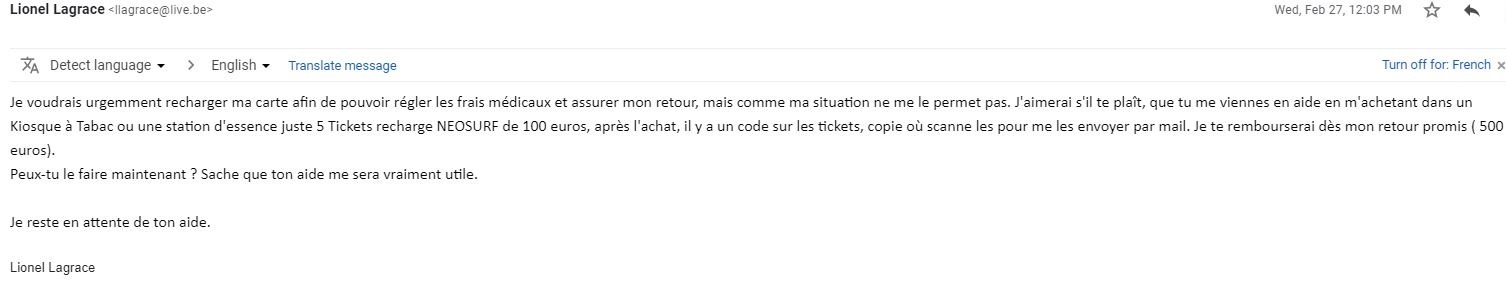
– ransom demand (example: by a so-called hacker who has taken you from a pornographic site and is asking for payment via Bitcoins, someone threatening to have a bomb placed on the company’s premises and asking for payment also via Bitcoins) Exemple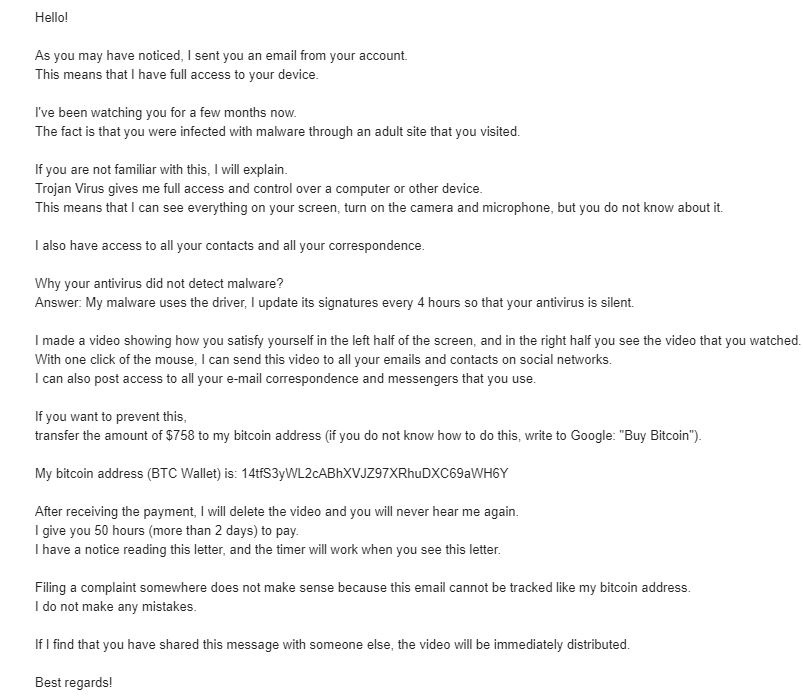
– drug sales proposal; Exemple
– proposal for an adult meeting from a so-called social dating network Exemple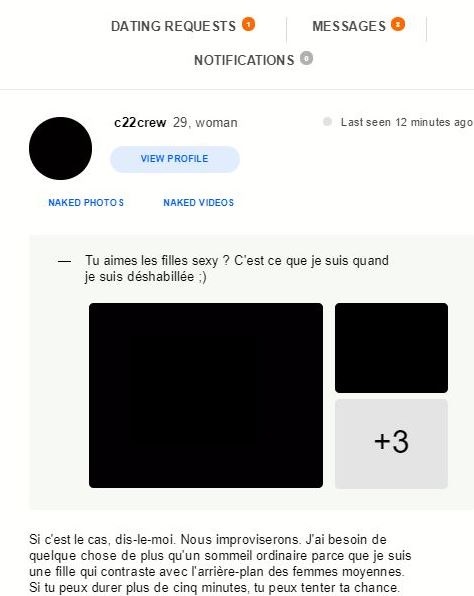
– mail that looks sent from your email address;
– email whose recipient’s address is not yours Exemple
– subject free email Exemple
– mail on a product you have not purchased asking you to click on a link or download an attachment Exemple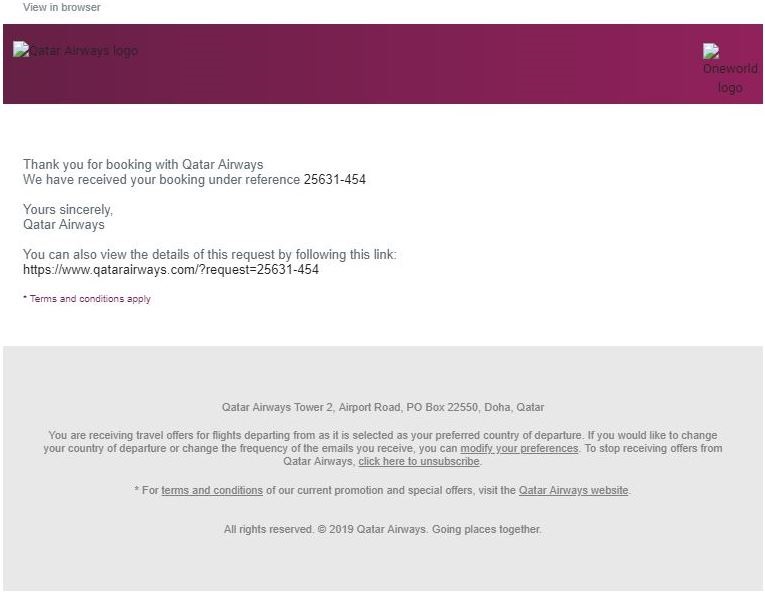
– mail written in a foreign language Exemple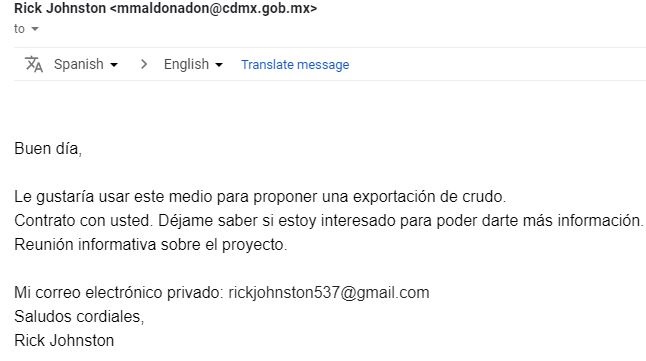
– person posing as your bank and asking you to put your card in the digipass so that you can connect to your bank account.
2. Some important rules to avoid a scam.
– never pay anything;
– avoid requests for money that would supposedly allow you to earn much more Exemple

– don’t pay attention to false evidence of money saving via PayPal Exemple
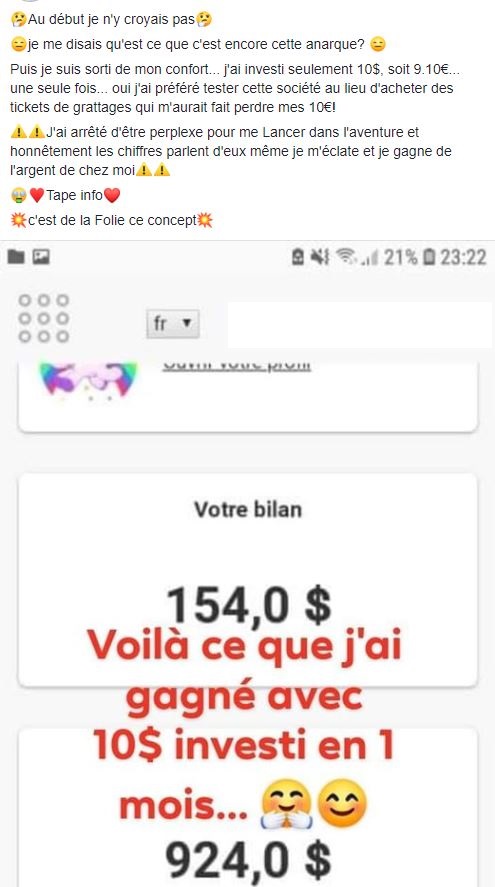 ;
;– look for as much information as possible about the company that contacted you;
– if something looks too good, unfortunately it is (you don’t make money easily for 2 clicks) Exemple
 ;
;– do not pay by bank account when purchasing a second-hand product to an individual who offers to send it to you by a delivery service but rather prefer hand delivery or payment via PayPal;
– always check to see if the address of the site you are at looks credible before using it Exemple
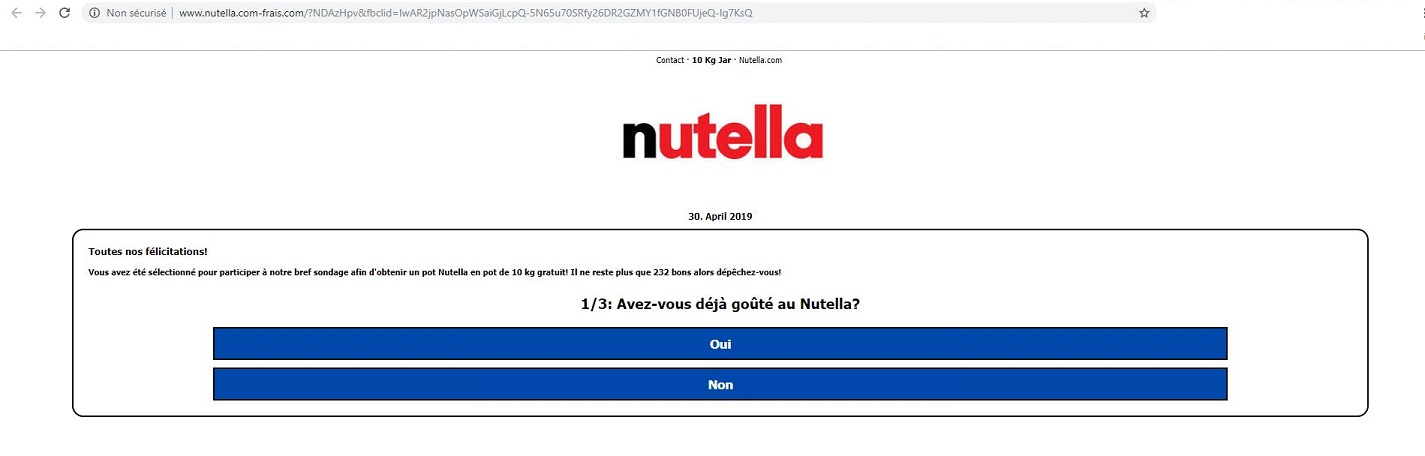 ;
;– check if the site you are on is protected by an SSL certificate with a padlock and its address that must start with https instead of http if not, avoid making a purchase or transmitting your personal data there Exemple
3. Small non-exhaustive list of scams.
Since the advent of the Internet and scams (scams) there are fortunately some well-known scams; that is why we will mention here the most known/common ones.
1. Fraud 419 (Nigerian fraud).
This well-known scam has several forms.
The common point is usually that the person is contacted by someone located abroad.
This person will say that he/she is either an heir to a large fortune, an employee of a bank or a dying person with a large amount of money (often several million) that he/she wishes to leave.
This scam therefore consists in offering you a large part of the money or all the money in exchange for your help to pay so-called fees.
As long as you agree to continue the scam will continue because of course to give you the promised amount there will always be a paper missing that you have to pay. Of course, you will never see the money or get yours back.
This scam can be either in your language or in a foreign language. It is mainly distributed by email.
2. Online shopping fraud.
This scam consists in selling you a fictitious product such as (medical device, photocopier, mobile phone, car etc…) at a very attractive price and well below the real value of the product.
In general, the seller will ask you to pay the amount of money through a money transfer service such as Western Union or prepaid cards.
This scam is usually distributed by email or when you visit a website, by a popup.
You can also find them on social networks such as Facebook or other and on sales sites between individuals such as 2ememain.be.
To protect yourself against it, always refuse to pay anything and, above all, never give out your personal information.
3. Emotional fraud.
This scam is very simple and consists in stealing from you by playing on your feelings.
The person will contact you mainly by email posing as someone you know who is in a dangerous situation such as:
– lack of money to pay for medical expenses
– lack of money to be able to return home following a theft of his money
– request for money following a humanitarian or other disaster that was well covered by the press (hurricane, destruction of a heritage such as Notre-Dame de Paris, etc.).
To protect yourself from it, you will have to understand that this person is in no way a person you know.
The person will often ask you for money via prepaid cards, cryptomones or Western Union and MoneyGram.
If you have read everything correctly and think you know how to recognize a scam, don’t forget to do our Quizz.



